Comparison of in-silico and in-vitro studies of benzimidazoleoxothiazolidine derivatives as m. Tubcerculosis transcriptor inhibitors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/gjpb.2023.2.6Keywords:
molecular docking, molecular dynamics, thiazo-benzimidazole, anti-tuberculosisAbstract
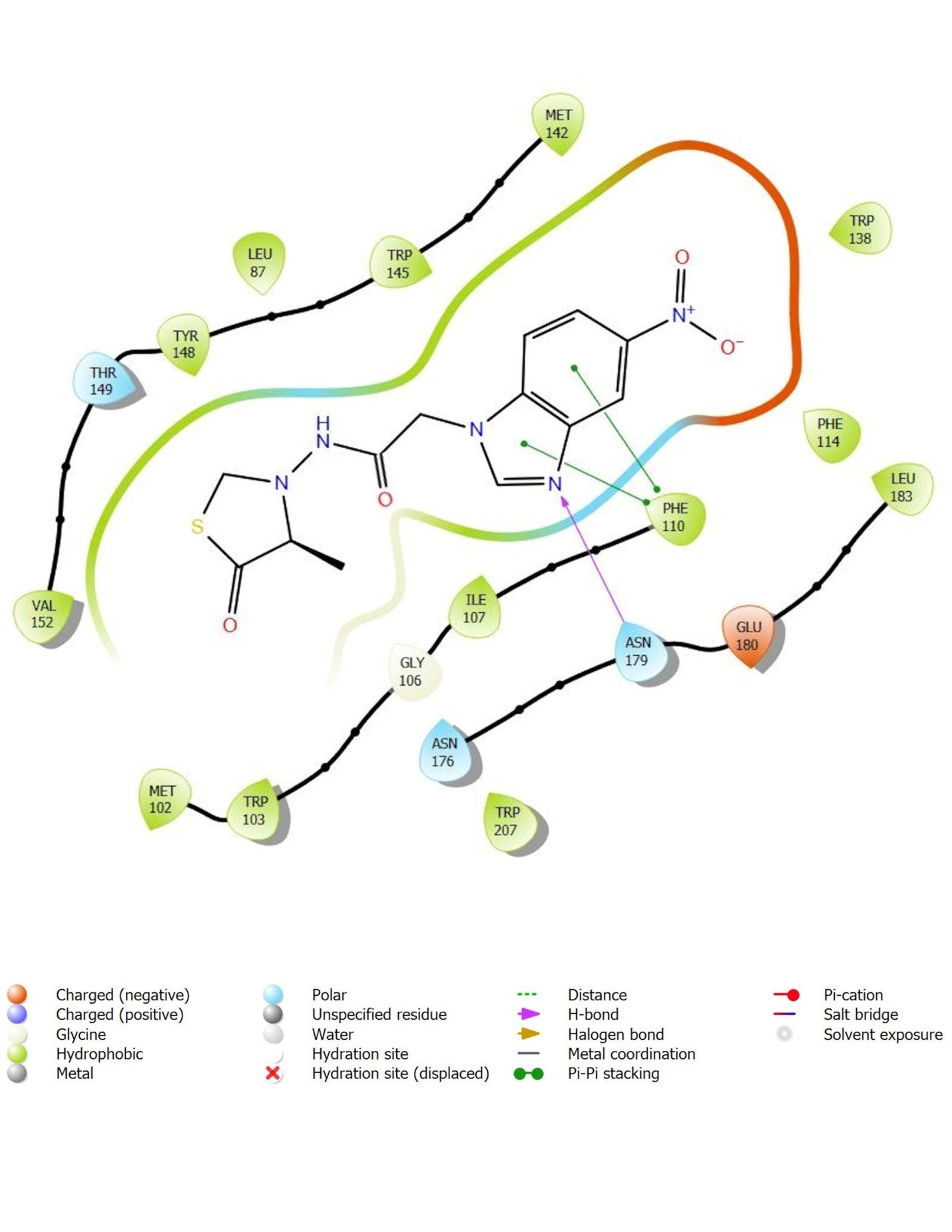
Novel N-(4-alkyl-4-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl)-2-(5-nitro-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)acetamide derivatives were evaluated as M. tuberculosis transcription inhibitors using protein 3Q3S, by performing molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. Twelve promising candidates exhibiting good binding interactions in the form of hydrogen bonds, pi-cation interactions, pi-pi stacking and low binding energies (-7.576 kcal/mol to -5.038 kcal/mol) were selected for wet lab synthesis. Their invitro anti-tubercular activity tests using Microplate Alamar Blue Assay were compared with insilico studies. Compounds 4a, 4b, and 4g have exhibited good activity with MIC values of 1.6 μg/ml, while the other compounds exhibited activity at MIC values of 3.125-6.25 μg/ml. The results show that the presence of an additional H-bonding group at the ortho position in the substituted aryl group attached to the thiazolidine ring is leading to an increase in the activity owing to an increase in the binding interaction of the molecule to the substrate.
Metrics
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Sonal dubey , Sakshi Bhardwaj, Prabitha Prabhakaran, Subhankar Parboth Mandal, Ekta Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







