Ophthalmology: Navigating ocular barriers with advanced nanocarriers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/gjpb.2024.3.10Keywords:
Ophthalmology, Ocular Barriers/ ocular drug delivery, Glaucoma, Age-related Macular Degeneration, Diabetic Retinopathy, Ocular Diseases,, NanocarriersAbstract
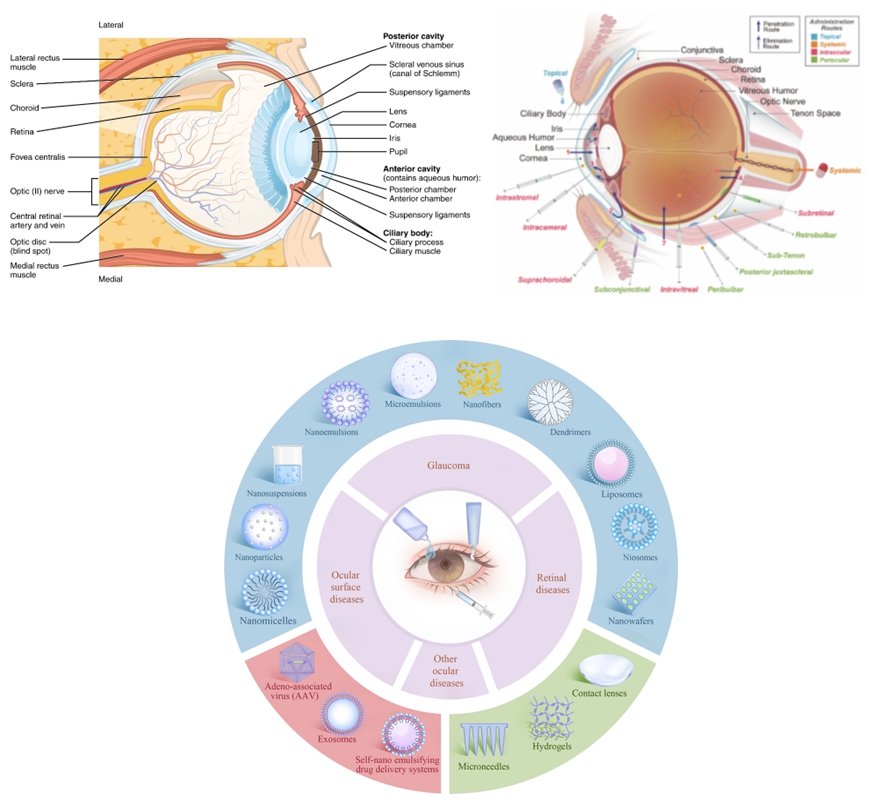
The unique anatomy and physiology of the eye present significant challenges for effective drug delivery, necessitating innovative approaches to manage ocular diseases. This review examines the intricate structure of the eye and the barriers that impede drug penetration, including the corneal epithelium, conjunctival tissue, and blood-retinal barriers. Traditional ocular administration routestopical, periocular, and intraocular-often face limitations in drug bioavailability and patient compliance. Recent advancements in nanotechnology offer promising solutions to these challenges. Nanocarriers such as nanoparticles, liposomes, nanosuspension, nanoemulsion, micelles, and dendrimers enhance drug delivery by improving bioavailability, controlling release rates, and minimizing systemic side effects. Factors influencing the efficacy of these nanocarriers include their size, surface charge, and hydrophilic-lipophilic balance. This review highlights the potential of these novel drug delivery systems in treating chronic ocular conditions such as glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and diabetic retinopathy. These advanced technologies are poised to significantly enhance the therapeutic management of ocular diseases by overcoming the inherent ocular barriers and optimizing drug delivery.
Metrics
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sanaul Mustafa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







